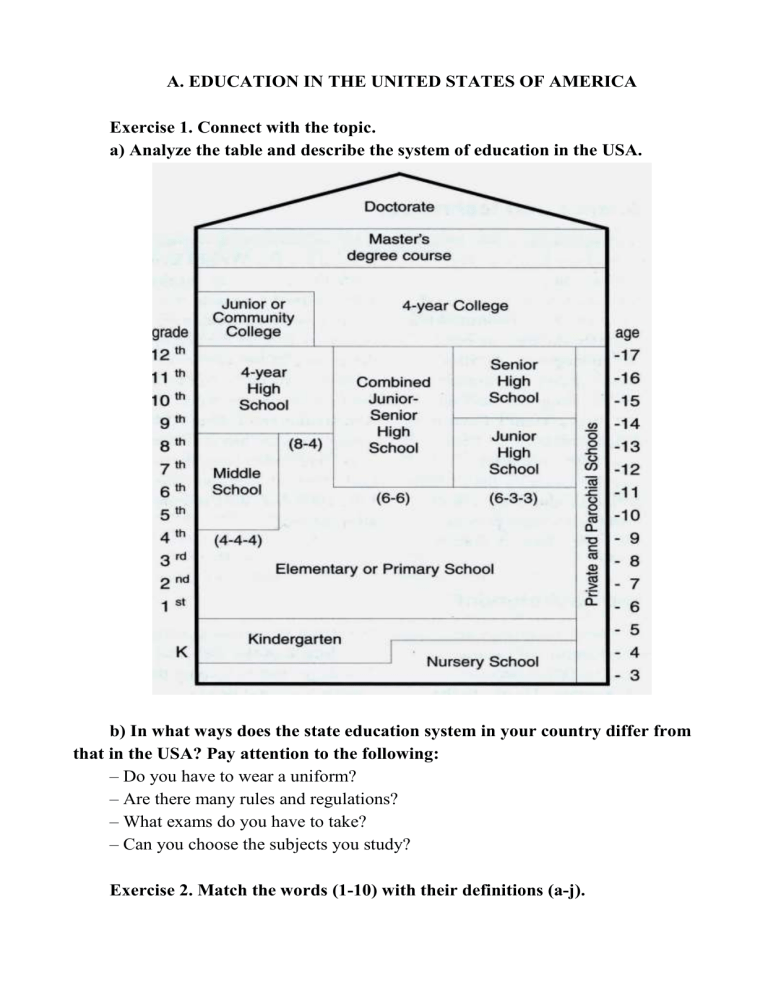
A. EDUCATION IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. a) Analyze the table and describe the system of education in the USA. b) In what ways does the state education system in your country differ from that in the USA? Pay attention to the following: – Do you have to wear a uniform? – Are there many rules and regulations? – What exams do you have to take? – Can you choose the subjects you study? Exercise 2. Match the words (1-10) with their definitions (a-j). 1. responsibility 2. 3. compulsory available 4. 5. 6. to attend to complete fee 7. 8. 9. 10. private to measure to be founded loan a. the money you pay for service from schools, universities, doctors b. money that something /somebody lends you c. the state or fact of being accountable or to blame for something d. to go to or be present at a place e. that must be done by rules, law f. owned, done or organized by a person or company, and not by the government g. to start an organization or institution h. to finish something i. that you can get, buy, use j. to find the size, weight, etc. of somebody/something often using an instrument Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps with the words from Exercise 2. 1. The prices for education are _______ in our country. 2. You should take ______ for this accident. 3. Samara State Technical University _____ in 1914. 4. He _____ his PhD next year. 5. The length of the wire _____ during the previous experiment. 6. He didn’t _____ classes and failed his exams. 7. Our daughter goes to a _____ kindergarten. 8. They decided to take a huge_____ from the bank for their new business. 9. Some subjects are _____ in the curriculum. 10. Tuition ______ increase due to inflation. Exercise 4. Read the text about the system of education in the USA and point out the key ideas of American education. Education plays a very important role in American society. It often determines a person's social role and standard of living. Education is a state responsibility. No wonder then that the laws and standards of education provided in individual states differ. In most states, education is compulsory from the age of 6 to 16. The atmosphere at elementary schools is usually friendly. Teachers keep to the idea that children's happiness and interest are the two most important things. Full secondary education up to the age of 18 is available to everyone and the number of young people, who stay at school until they are 17 or 18 is relatively high. Schools are comprehensive and are called high schools. Pupils can choose all kinds of subjects, from Development Reading to Problems of Democracy or Public Speaking. State schools prevail; not many pupils attend private schools. While secondary education is based on the idea of mass education with equal opportunity for all, higher education is extremely competitive and selective. It is not enough to have a high school diploma and an interview to be admitted to a college or a university. (Colleges provide undergraduate education leading to the bachelor's degree, while universities provide both undergraduate and graduate education leading to the master's and doctor's degrees.) There are two tests, which are used by universities as standards for comparison: the SAT (Scholastic Aptitude Test, which measures aptitudes in verbal and mathematical fields) and the ACT (American College Testing program, which measures skills in English, mathematics, and the social and natural sciences). Because there are many colleges and universities in the United States, quite a large number of high school graduates do have an opportunity to get a higher education. But completing university studies is very difficult. On the average, only about half of the bachelor degree students complete full four-year courses. Tuition fees are rather high at American universities, especially at private ones, and federal loans are not very big. That is why a majority of the students take on parttime jobs. Harvard, Yale and Princeton are the most prestigious private universities in the Eastern United States. On the West Coast, the University of California at Berkeley and the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) are held along with Stanford University in Palo Alto near San Francisco. The oldest American school is Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Boston. It was founded in 1636 by John Harvard, who was born in London and whose parents came from Stratford-upon-Avon in England. Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Образование, уровень жизни, доступный, общеобразовательная школа, среднее образование, возможность, способность, общественные науки, закончить, престижный, отличаться, естественные науки, плата за обучение, навык, работа неполный рабочий день, закон, преобладать, в среднем. Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations. 1. part-time a. studies 2. elementary b. degree 3. equal 4. master’s 5. measure 6. natural 7. tuition 8. federal 9. complete c. loans d. school e. fee f. opportunity g. job h. aptitudes i. sciences b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) in the correct form and answer the questions. 1. What was the atmosphere like when you studied at the _____ school? 2. Do you pay _____ fees for your education at the university? 3. How can _____ be measured? 4. Does our state provide any _____ loans for education? 5. Do any of your groupmates take on _____ jobs? 6. Do young people in our country have _____ opportunity to choose the university they like? 7. Does your department provide master’s _____? 8. What year will you complete your _____ at the university? 9. What natural _____ do you study at the university? Exercise 7. Are the sentences True or False? 1. Standard of living doesn’t depend on education. 2. There is no difference between laws and standards of education in different states of America. 3. The number of young people who get full secondary education is high. 4. Pupils are not allowed to choose subjects. 5. There are no private schools in the USA. 6. Higher education is competitive and selective. 7. It is enough to have a high school diploma to be admitted to a college or a university. 8. Not all students complete full four-year courses. 9. Education at American universities is free of charge. 10. Harvard University is the oldest in the USA. Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. At what age is education compulsory? 2. What level of education can students choose subjects at? 3. What do high school graduates need to enter: a college or a university? 4. What percentage of bachelor degree students complete full four-year course? Why? 5. Why do the university students take on part-time jobs? 6. What is the most important principle of education at elementary school? at high school? at a university? Exercise 9. Match the phrases to the prepositions. 1. to be good a. in 2. to be afraid b. on 3. to be worried c. at 4. to be terrible d. about 5. to be interested e. of 6. to be fond f. at 7. to be keen g. of b) Complete the sentences with an adjective and preposition so that they mean the same as the sentence above. 1. At school, Tom Cruise did well at sports. At school, Tom Cruise was good at sports. 2. Other kids laughed at Bill Gates because his only interest was computers. Other kids laughed at Bill Gates because he was only_____ computers. 3. Kurt Cobain didn't like school, but he really liked his art teacher. Kurt Cobain didn’t like school but he was_____ his art teacher. 4. At his school, Tiger Woods was frightened by the other boys. At his school, Tiger Woods was _____ the other boys. 5. Winston Churchill hated school, but he loved reading. Winston Churchill hated school, but he was very_____ reading. Exercise 10. Complete the text with the right form of the verbs (active or passive). Degree-granting institutions in the United States _____ (call) colleges, institutes or universities. As a general rule, colleges _____ (be) smaller and usually _____ (offer) only undergraduate degrees, while a university also _____ (offer) graduate degrees and may include several colleges. Most of them are 4-year institutions. The words "school," "college," and "university" often _____ (use) interchangeably. An institute usually _____ (specialize) in degree programs in a group of closely related subject areas, for example, institutes of technology, institutes of fashion, institutes of art and design, and so on. Institutes may also be part of universities. Within each college or university schools _____ (find), such as the school of arts and sciences or the school of business. Each school is responsible for the degree programs offered by the college or university in that area of study. Exercise 11. Complete the text with the right form of the verbs (active or passive). Community colleges in the USA _____ (provide) two-year associate degree programs, as well as excellent technical and vocational programs. They ______ (call) the associate of arts (A.A.) or associate of science (A.S.) degrees. As the name _____ (suggest), community colleges _____ (be) community-based institutions with close links to secondary schools, community groups, and employers, and many U.S. students _____ (live) close to campus with their families. Community colleges can be public or private institutions and sometimes _____ (call) junior colleges or two-year colleges. A growing number of international students _____ (choose) to study at community colleges. Tuition costs _____ (be) often lower at two-year than at four-year institutions and many _____ (have) agreements to allow students to move easily into the third year of a bachelor's degree at the local state university. Exercise 12. a) Read the following comments made by students and decide whether each is for or against taking exams. Complete the sentences with the right form of the verbs. 1. Exams _____ (make) everyone try to get the best marks they can. 2. I _____ (feel) well during the exam, so I _____ (not do) well. 3. The boy sitting next to me _____ (study) at all, but he _____ (copy) my answers and _____ (pass) the exam. 4. I _____ (not think) I’d bother studying if we didn’t have exams. 5. I _____ (write) very slowly, so I hardly ever have enough time to finish an exam. 6. I use my exam grades to find out whether or not I _____ (improve) in a subject. 7. I think exams _____ (be) the quickest way of testing students. 8. I _____(study) for weeks before my last exam, but on the day itself I was so nervous that I couldn’t remember a thing. b) Write the reasons for and against in the boxes, as in the example. FOR AGAINST Exams encourage students to work Exam results may depend on how harder you feel on a particular day Exercise 13. Read the text and draw a chart about higher education structure in the Russian Federation. In Russia higher education is provided by state and non-state higher education institutions (HEIs). The Federal Agency for Education finances half of state HEIs. The rest ones are financed by other Ministries or local authorities. Approximately half of the State HEIs students pay for their studies. In nonstate HEIs all students have to pay tuition fees. Higher education is within the Ministry of Education and Science’s jurisdiction. The Federal Service of Supervision in Education and Science is responsible for quality in education. There are two levels of higher education: 1) 4-year programs leading to the Bachelor’s degree, the first final university degree; 2) postgraduate studies with duration of 1-2 years leading to the Specialist Diploma or the Master’s degree. HEIs are authorized to award the Master’s degree after the completion of 2 years of study or the Specialist Diploma after 1 year of study following upon the Bachelor’s degree. Scientific degrees in Russia traditionally include two levels of doctoral degrees: the Candidate of Sciences (the first level, equivalent to PhD) and the Doctor of Sciences (the second, highest level). Exercise 14. Compare what you believe to be the strengths and weaknesses of American education system with your own. Start the sentences with the phrases below. Firstly Secondly A comparison between In comparison with/to As compared to Differences and similarities between Similarly Unlike Whereas On the one hand ………… , on the other hand …………….. . In conclusion Exercise 15. Watch a video “What's It Like Inside Stanford University? | Stanford Campus Tour” and answer the questions. ( https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=emBoDloCze8) 1. What is the iconic building in Stanford University? 2. What do the numbers on the floor mean? 3. What can be seen in the invidio auditorium? 4. What is fountain hopping? 5. How do students spend their free time? Exercise 16. Develop presentation material about your university structure based on the video in any of these formats: advertisement, guide for newcomers, new website. Exercise 17. Make the Internet search on five leading USA universities and complete the table. University Date of Mission Schools Famous Flag, Interesting establish statement graduates motto, facts ment emblem B. HIGHER EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. Analyze the chart and describe the system of education in Great Britain. In what ways does the state education system in your country differ from that in England? Exercise 2. Match the words (1-10) with their meaning (a-j) 1.school leaver a. to give somebody/something a name 2.to admit b. the desire or need for something 3.full-time course 4. to fail 5. demand 6. expansion 7. to establish 8. to name after 9. to site 10. research c. to put or build something in a particular place d. for a whole of the normal period of study e. a detailed and careful study of something to find out more information about it f. a person who has just left school g. the process of becoming greater in size, number, or amount h. to allow somebody to enter, to take somebody into a place i. to start something (an organization or institution) j. to unsuccessful in something Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps using the words from Exercise 2. 1. She _____ to college without exams due to her natural aptitudes. 2. The board _____ detailed criteria for candidates. 3. There is the lack of job opportunities for _____. 4. The sportsground _____ behind the school. 5. The university _____ the prominent scientist. 6. Higher educational establishments provide _____. 7. Scientists predict a new period of economic _____. 8. There is always strong _____ for specialists in this branch of industry. 9. If students miss many classes, they _____ their exams. 10. Our group conducts ______ in physics. Exercise 4. Read the text about higher education in Great Britain and make up a list of the key ideas. Only about one third of school leavers in Great Britain receive post-school education, compared with over 80 per cent in Germany, France, the United States and Japan. However, it must be borne in mind that once admitted to university relatively fewer (15 per cent) British students fail to complete their degree course. Fourteen per cent of 18– and 19-year-olds enter full-time courses (degree or other advanced courses higher than A level). These courses are provided in universities, polytechnics, Scottish central institutions, colleges of higher (HE) and further (FE) education, and technical, art and agricultural colleges, non-advanced vocational training and educational courses. In addition, there are part-time students, who are released by their employers. Today there are forty-seven universities in Britain, compared with only seventeen in 1945. They fall into four broad categories: the ancient English foundations, the ancient Scottish ones, the ‘redbrick’ universities, and the ‘plate-glass’ ones. They are all private institutions, receiving direct grants from central government. Oxford and Cambridge, founded in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries respectively, are easily the most famous of Britain’s universities. Today ‘Oxbridge’, as the two together are known, educate less than one tenth of Britain’s total university student population. But they continue to attract many of the best brains, partly on account of their prestige but also on account of the seductive beauty of many of their buildings and surroundings. Both universities grew gradually, as federations of independent colleges most of which were founded in the fourteenth, fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. In both universities, however, new colleges have been established, for example Green College, Oxford (1979) and Robinson College, Cambridge (1977). In the nineteenth century many more redbrick universities were established to respond to the greatly increased demand for educated people as a result of the Industrial Revolution and the expansion of Britain’s overseas empire. Many of these were sited in the industrial centres, for example Birmingham, Manchester, Nottingham, Newcastle, Liverpool and Bristol. With the expansion of higher education in the 1960s many more plate-glass universities were established, some named after counties or regions rather than old cities, for example Sussex, Kent and East Anglia. There is also a highly successful Open University, which provides every person in Britain with the opportunity to study for a degree, without leaving their home. It is particularly designed for adults who regret missed opportunities earlier. It conducts learning through correspondence, radio and television, and also through local study centres. University examinations are for Bachelor of Arts, or of Science (BA or BSc) on completion of the undergraduate course, and Master of Arts or of Science (MA or MSc) on completion of postgraduate work, usually a one– or two-year course involving some original research. Some students continue to complete a three-year period of original research for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Высшее образование; нужно иметь в виду; будучи принятым в университет; профессиональное обучение; образовательные курсы; получать стипендию; привлекать лучшие умы; давать образование; предоставлять возможность; упущенные возможности; местные учебные центры; по завершении курса обучения; аспирантура; бакалавр естественных наук; бакалавр гуманитарных наук; магистр гуманитарных наук; магистр естественных наук; степень доктора философии, предоставлять, кроме того, работодатель, учреждение, из-за (вследствие), основывать, называть в честь, повышенный спрос, взрослый человек, включать в себя. Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations. 1. receive a. research 2. full-time b. training 3. complete c. education 4. private d. opportunity 5. increased e. leaver 6. regret f. course 7. school g. institution 8. vocational h. degree course 9. receive i. demand 10. original j. grants b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) in the correct form and answer the questions. 1. Do all students complete their ______? 2. What should one do to _____ a grant? 3. Why is it necessary to receive _____? 4. What branches of industry have an _____ demand for skilled specialists? 5. What degrees require an _____ research? 6. What private ______ can school leavers enter? 7. Where can senior-year students have their _____ training? 8. Is there a lack of opportunities for _____ leavers? 9. Have you ever regretted _____of not doing any special course? 10. Where can students take _____ courses? Exercise 7. Are the statements True or False? 1. Only about one third of school leavers receive post-school education. 2. Today there are fifty-seven universities in Britain. 3. Oxford and Cambridge were founded in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries respectively. 4. Open University provides every person in Britain with the opportunity to study for a degree without leaving their job. 5. Open University conducts learning only through local study centres. 6. University examinations are for Bachelor of Arts, or of Science on completion of the undergraduate course. 7. Most students continue to complete a three-year period of original research for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. How many universities are there in Britain? 2. What are the most famous Britain’s universities? 3. What categories of universities in Britain do you know? 4. What opportunity does Open University provide every person in Britain with? 5. Whom is Open University designed for? 6. In what way does Open University conduct learning? 7. What degrees do undergraduates receive? Exercise 9. Complete the text about the difference between College and University in the UK with the right form of the verb in the Passive Voice. Is there the difference between College and University in the USA? In the United Kingdom, the difference between college and universities _____ (define) very well. Colleges are specialized institutes of learning under aegis of a university. Courses _____ (teach) in colleges, but the degree _____ ( grant) by the university. University is the parent body and colleges adhere to its rules. Besides the colleges, research departments ______ (include) in the university structure. Exercise 10. a) Match the verbs with prepositions. 1. name 2. fall 3. respond 4. differ 5. go 6. divide 7. lead 8. specialize a. into b. in c. after d. on e. into f. to g. from h. to b) Translate the sentences using verbs with prepositions from a). 1. Некоторые студенты продолжают обучение для получения степени магистра. 2. Университеты Британии подразделяются на четыре большие категории. 3. Программы технических вузов отличаются от гуманитарных. 4. Некоторые университеты были названы в честь выдающихся ученых. 5. Я надеюсь, комиссия даст положительный ответ на мой грант. 6. Недавнее исследование в области дистанционного обучения привело к неожиданным результатам. 7. Учебный год в британских университетах и колледжах делится на 3 семестра. 8. Он специализируется в компьютерных технологиях. Exercise 11. Complete the text with the right form of the verbs (active or passive). The United Kingdom _____ (have) many higher education opportunities. The autonomy of higher-education institutions is striking. Its universities _____ (have) almost complete autonomy from the National or local governments. The state _____ (not control) university syllabuses, but it _____ (influence) admission procedures through the Office for Fair Access. There are three kinds of higher education institutions in Great Britain: universities, colleges of higher education and colleges of further education. Some young people who _____ (decide) to leave school at the age of 16 may go to a further education college, full-time or part-time. Further education colleges _____ (have) strong ties with commerce and industry. After three years of study, a university graduate _____ (leave) with the Degree of Bachelor of Arts, Science, Engineering, Medicine, etc. The degrees _____ (award) at public degree ceremonies. The Advanced Level General Certificate of Education (A-level) _____ (require) for admission to all kinds of higher education institutions. Good A-level results in at least two subjects are necessary to get a place at a university. Many universities _____ (choose) their students after interviews. The academic year in Britain’s universities and Colleges _____(divide) into 3 terms which usually _____ (run) from the beginning of October to the middle of December, the middle of January to the end of March, from the middle of April to the end of June or the beginning of July. Exercise 12. Correct mistakes in the following sentences. 1. Open University was found in 1969. 2. This college has be established recently. 3. The difficult job will do by specialists. 4. Our university was name after a great writer. 5. Local study centers and residential summer schools are sponsoring by the Open University. 6. Usually tests used by universities to measure students’ knowledge. 7. They will be admit to the university without exams. 8. Extension courses at the Open University is taught through television and radio programs. 9. Students’ essays was checked by the teacher. 10. The students numbering not more than four are instruct by a Don (a university tutor) at Oxbridge. Exercise 13. Read the text and say what you call - the money some students receive if they get a place at university; - the qualification you get at the end of university; - the name we give students during this period at university; - teachers at university; - students when they have completed their first degree; - students studying for a second, higher degree; - the study of one subject in great depth and detail, often to get new information; - the talks/lessons that students go to while they are at university. Studying at (a British) university If you want to go to university, you must first pass examinations that most students take at the age of 18 (called ‘A’ levels). Students usually take three or four ‘A' levels (examinations in three or four subjects), and they must do well to get a place at university. If you get a place, most students have to pay part of their tuition fees. Some students also get a government grant, but most students need a loan to cover the cost of university life. Students at university are called undergraduates while they are studying for their first degree. Most university courses last three years, some courses last four years, and one or two courses, e.g. medicine, are five years. During this period students can say they are doing a degree, and when they finish and pass their exams, they can say they have a degree. This can be a BA or a BSc. For example: He hopes to get a place at Oxford. She's at university in Glasgow. She's doing a degree in physics. I've got a degree in German from York University. She's got a BA in French. He's got a BSc in computer science. Postgraduate courses When you complete your first degree, you are a graduate. Some students then go on to do a second course or degree, called a postgraduate course/degree These students are then postgraduates and they often study for: an MA (Master of Arts) e.g. I'm doing a Masters in English or an MSc (Master of Science) e.g. She did a Masters in biology or a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) [minimum three years] e.g. He's got a PhD in computer science. When people study one subject in great detail (often to find new information), we say they are doing research, e.g. My sister is doing research into/on the effects of stress at work. Exercise 14. Watch a video “Higher Education in the UK” (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1IYy_xZEdPg) and answer the questions. 1. Why do students come to British Universities? 2. What are the traditions at Oxford University? 3. What subjects are taught at King’s college London? 4. What events do students organize? 5. Are students successful at finding jobs after British Universities? Exercise 15. Make the Internet search on five leading British universities and complete the table. University Date of Mission Schools Famous Flag, Interesting establish statement graduates motto, facts ment emblem Get ready with the presentation “Essential Features of Education Abroad” Consider the following points: - the role of education; - rules and regulations; - types of higher education institutions; - tuition fees; - the organization of the academic year; - the most prestigious universities. C. THE WAYS OF GETTING EDUCATION AND PROFESSIONAL SKILLS Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. What would you prefer: - to do a course you enjoy OR to do a course that leads to a good job? - to study in your home town and live with your parents OR to go to a university in a different city? Why? - to do what your parents think is best OR to do what YOU want to do? - to start work straight after graduating OR to travel around the world a bit? - get a job after you leave school OR to go straight to university? Exercise 2. Match the words with their meaning 1.digital a. comprehensive and extensive course covering many topics, communication offering an overview of the field 2. to take up b. a form of training which is provided at the work place during the performance of the actual job 3.broad-based c. electronic transmission of information that has been encoded course digitally 4. fault d. a person who is learning a trade from a skilled employer 5.applied science e. to use or fill an amount of time or space 6.defense industry f. the application of existing scientific knowledge to practical applications 7. skilled g. government and commercial industry involved in research, development, production, and service of military materiel, equipment and facilities 8.on-the-job h. having or showing the knowledge, ability, or training to training perform a certain activity or task well 9. to obtain i. something wrong or not perfect in a thing or person’s character 10. apprentice j. to get something Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps using the words from Exercise 2. 1. The mechanic found a_____ in the car within a few minutes. 2. Nowadays employers try to hire _____ specialists. 3. More and more people use _____ in their everyday life. 4. My grandfather started off as _____ and now he is an executive of a big company. 5. He _____ this position after graduating from the college. 6. What education is needed to work in the _____? 7. The university offers undergraduate programs in _____. 8. Sorry for interrupting you, I won’t ______ too much of your time. 9. Continuous _____ is provided to the staff as part of the company project. 10. If you don’t want to focus on a special area, you’d better start with _____. Exercise 4. The texts describe different ways of studying technology. Read and note the information. 1. Which way of studying technology does your text describe? 2. Why did the student choose this way? 3. What kind of courses do the students take? 4. How long does it take to complete their study? 5.What kinds of jobs can they do when they complete their studies? University Christina is a second-year student of Electronic engineering at university. She decided to study at university because she wants the best choice of career and because she's interested in doing research in digital communications in particular. Most degrees take three years to complete, but some take up to five years because they include periods of work experience. Degrees may have a broad focus, for example Electrical engineering, or focus on a specialized area, such as Power and High-voltage engineering. Christina's course is broad-based to start, but she can specialize in digital communications later. Engineering can be studied in combination with other subjects. Christina is taking German because she wants to spend six months in a German telecommunications company. This work experience will earn her credits towards her degree. There is a wide career choice for graduate Engineers in design, production, quality assurance, and other fields. They may also work in marketing or become managers. Christina hopes to become a Research Engineer, finding new and better ways of doing things. Technical College Okan is a first-year student at a technical college. He chose to study full time because he wanted to get a qualification before he started work. He thinks that being at college will give him more time to decide exactly which career he wants to follow and that having a qualification first will help him to get the kind of job he wants. Colleges offer a wide range of vocational qualifications. Courses combine applied science, practical skills, and technical know-how. An Electronics Technician, for example, studies physics to understand the principles of the subject, learns how to find faults in equipment, and acquires a great deal of knowledge about electronic devices and components. Courses also include Communication skills to help students deal with communication at work and with the public. College courses may take a year for a certificate and two years for a diploma. When he graduates, Okan can start work as a Technician or go on to further study at university. Apprenticeship Alessandro has just started as an apprentice Aircraft Fitter with a large defense industry company. Apprenticeships are a way of combining work with practical training. He chose an apprenticeship because he wanted to leave school and start working and earning money as soon as possible. Today, apprentices combine work, on-the-job training, and part-time study on a day-release basis at a local college, paid for by their employer. Apprenticeships last from one to three years. In Alessandro's case, over the next two years he can obtain vocational qualifications to become a skilled Technician. He can also study to obtain entrance qualifications for higher-level studies so he can go on to become an Aeronautical Engineer. Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. В частности, интересоваться; опыт работы; достигать чего-либо; начинающий; оборона; работодатель; приобретать опыт; заканчивать институт; широкая специализация; профессиональная квалификация; заочное обучение; зарабатывать деньги; совмещать, выбор карьеры, большое разнообразие, электротехника, опыт работы, оборудование, устройство, иметь дело с, местный, удостоверение (свидетельство) Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations. 1. work a. money 2. combine 3. practical 4. full 5. earn 6. do 7. wide b. experience c. work d. time e. skills f. range g. research b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) and answer the questions. 1. What practical _____ can students get at the university? 2. Do you think that students should have a period of work _____ at the university? 3. Is it difficult to _____ work with studies? 4. What education is better _____ time or part time? 5. Does your university offer a wide _____ of qualifications? 6. What areas can students do ______ at your university? 7. Can students _____ money while studying at the university? In which way? Exercise 7. Are the statements True or False? 1. Christina decided to study to earn money as soon as possible. 2. She is interested in digital communications. 3. All degrees take three years to complete. 4. Christina studies German because she wants to live in Germany. 5. There is a wide career choice for graduate engineers. 6. Okan studies part-time. 7. Having a qualification helps to get the job you want. 8. Colleges provide vocational qualifications. 9. Alessandro is an apprentice in a telecommunications company. 10. Employers pay for education. Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. Why did Christina decide to study at university? 2. What subjects does Christina study? 3. What is she going to be? 4. Why is Okan studying at college? 5. What can colleges offer? 6. Where does Alessandro work? 7. Can he work and study at the same time? Exercise 9. Report these quotes. Use the words: explained, said, assured, warned, announced, told, mentioned. 1. “An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.” (Benjamin Franklin) 2. “Education is the passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to those who prepare for it today.” (Malcolm X) 3. “Education is what remains after one has forgotten what one has learned in school.” (Albert Einstein) 4. “Formal education will make you a living; self-education will make you a fortune.” (Jim Rohn) 5. “Wisdom…. comes not from age, but from education and learning.” (Anton Chekhov) 6. “The main hope of a nation lies in the proper education of its youth” (Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus) 7. “Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at twenty or eighty. Anyone who keeps learning stays young. The greatest thing in life is to keep your mind young.” (Henry Ford) 8. “The illiterate of the 21st century will not be those who cannot read and write, but those who cannot learn, unlearn, and relearn.” (Alvin Toffler) Exercise 10. a) Match the verbs with prepositions. 1. work a. with 2. deal b. up 3. graduate c. for 4. pay d. in 5. take e. from 6. involve f. with 7. compete g. in b) Translate the sentences using verbs with prepositions from a). 1. Институт занимается исследованием и разработками. 2. Выпускники конкурируют друг с другом на рынке труда. 3. Выпускники университета работают во многих промышленности. 4. В статье рассматриваются проблемы высшего образования. отраслях 5. Билл Гейтс окончил Гарвардский университет. 6. Получение степени занимает 4 года. 7. Многие студенты оплачивают свое образование. Exercise 11. Read the text “Student Mobility” and answer the questions. 1. What is student mobility? 2. Why are such students preferred? 3. What are the advantages of studying abroad? 4. What is the problem with student mobility? Student mobility is the overseas movement of students, which helps them to improve their employability skills, develop international networks, broaden their cultural outlook, learn in a different environment and gain a new perspective. National governments support the idea of international education and recognize the benefits that their students get while studying overseas. Students who graduate with internationally relevant degrees are required by industries, companies and other enterprises in their own countries. They help their countries to compete internationally. Therefore, those students are preferred employees everywhere and employers indicate that an overseas study experience is becoming more and more important. Fortunately, all the credits earned at overseas universities are accepted in transfer by universities back home. There are many student-exchange programs, which are a vehicle for those young people who are keen to experience education abroad. These programs do not just provide opportunities to take courses in other institutions, but also to experience how these courses are taught elsewhere. If the exchange program is in an overseas institution, students get the benefit of experiencing life in a different country, living in a different culture or among several cultures, learning a foreign language. For those who are interested in this option, funding may be the only problem, as many exchange programs generally require that the exchange students pay their own way to and from the overseas institution. The expenses can come up to a large sum including the prices of return air tickets, travel, and room and board. Exercise 12. Imagine that you are going to study abroad. Tell about your future journey. 1. What are my objectives and reasons for wanting to study overseas? 2. What are my academic and career goals? 3. How will I finance 6 months or a year overseas? 4. When will be the best time to go abroad? 5. What are my outside interests? (Student Governments; sport competitions; Volunteer Activities (rebuilding homes, planting trees, etc.); Multicultural Activities; plays; musicals; dance concerts; singing groups; Religious organizations; Media organizations) 6. What sort of accommodation do I want to live in? (Family homestays; university halls of residence; independent hostels; private rented accommodation) 7. What are my language skills? (My English is fluent and accurate; I can speak English with some confidence; I have a good basic ability to communicate and understand; I can communicate in a very basic way; I have never studied English) Exercise 13. In each of the following sentences there is a mistake. Find it and correct it. 1. She told me that she is an apprentice with the construction company. 2. The tutor told we that exams measured a small part of a person’s abilities. 3. The dean asked me what science subjects I have chosen. 4. She asked me if I want to attend this conference. 5. My friend advised me don’t take a gap year. 6. He told me he has had practice in a big plant. 7. The interviewer wondered if my English is fluent. 8. The employer assured my work experience will earn me credits. 9. He asked me how has technology improved the educational system. Exercise 14. Watch a video “Apprenticeship: Building Your Career” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DU6jEK7coc0 and answer the questions. 1. Why is an apprenticeship also called ‘earn as you learn’? 2. What do apprentices learn in the classrooms? 3. How long does it take to complete an apprenticeship? 4. What are the reasons to choose the apprenticeship path? 5. Who can be an apprentice? Exercise 15. Make a report on your university referring to its website and highlight the following points: mission statement, departments, degrees, ratings, etc. D. ENGINEERING EDUCATION Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. - What department do you study at? - Who helped you to make a choice? - What subjects do you study? - What subjects are you good at? - What personal traits are required for your future job? - What are the career opportunities for the graduates of your department? Exercise 2. Match the words with their meaning 1. top-rated a. the skills and abilities that allow you to be employed 2. to benefit b. considered to be the best or among the best 3. requirement c. requiring great effort and determination 4. advantage d. the temporary posting of someone in a workplace to enable them to gain work experience 5. challenging e. something that you need or that is demanded 6. processing f. to perform or carry out a duty or task 7. failure g. the carrying out of operations on data, especially by a computer, to retrieve, transform, or classify information 8. employability h. to receive an advantage; profit 9. placement i. nonperformance of something required or expected 10. to fulfill j. a way in which one thing is better than another Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps using the words from Exercise 2. 1. The accident was caused by engine _____. 2. All the conditions _____ in the experiment. 3. Both countries _____ from the treaty. 4. He was good at solving _____ problems. 5. Our company is one of the 10 _____companies in the region. 6. The department I work in deals with the _____ of data. 7. If you are unemployed you should consult a job _____ expert. 8. Before entering the university study the entrance _____. 9. The university tries to provide _____ for its graduates. 10. This system has one great _____ over other ones. Exercise 4. Read the information from the university prospectus and compare it with your own university. Make a list of university subjects. Welcome to the Department of Mechanical Engineering The Department of Mechanical Engineering at Imperial College London is one of the largest and most advanced departments in mechanical engineering in the UK. We were the top-rated Department of Mechanical Engineering in the recent Research Assessment Exercise 2008, held by the UK Government. Mechanical engineering continues to play a key role in developing, operating and manufacturing new machines, devices and processes to benefit mankind. Mechanical engineers apply their creative imagination and professional skills to combine both theory and practice in a variety of situations. For this, they need an in-depth understanding of scientific principles and engineering processes. They also need to be able to develop solutions to real-life problems in the face of conflicting requirements. Mechanical engineers in the commercial world combine technical and management skills to retain the competitive advantage for their companies. The overall mission of the Department is to deliver world-class scholarship, education and research in Mechanical Engineering, with particular regard to their application in industry, healthcare and commerce. Mechanical engineering study is an excellent springboard for careers not only in engineering, but also in many other challenging fields. There is a lively and consistent demand for our graduates from a broad spectrum of industrial, government and commercial organizations. First and second years. During these years, a careful mix of lectures, practicals and case studies develops your understanding in: mechanical engineering (engineering design, mechanics, modelling and mathematics); professional skills (teamwork, communication and management); and materials (the properties, selection, processing, failure and protection of metals, polymers, ceramics and composites). These are related to industries such as aerospace, automotive, sports, and power generation. At the end of your second year, a ten-week, paid industrial placement allows you to put these skills into practice; eligible students can choose the special programme, which involves a six-month industrial project in the fourth year. Third and fourth years. The third year advances your understanding of mechanical engineering whilst you gain specialist knowledge in areas of materials, such as aerospace, sports and biomaterials, that interest you most. You also take part in an individual research project or a multidisciplinary project. Year in industry. We help and encourage you to gain work experience in an engineering firm. Industrial experience increases your employability, helps you to choose your career path and increases your motivation to succeed in your chosen profession. This could be a placement between your second and third years, a single semester of the fourthyear project, a summer vacation job, or a gap year between school and university. Career opportunities. Our many close industrial links mean that your employment prospects are excellent. On graduation you will have the specialist knowledge, understanding and transferable skills needed to fulfill a challenging and rewarding career in any industry making or using materials; such as, for example, Rolls-Royce, Jaguar Cars, GSK and Corus. Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Факультет машиностроения; за последние годы; одни из лучших; играть важную роль в развитии; соединить теорию и практику; находить решения проблем в жизненных ситуациях; приносить пользу компании; давать стипендию; применение в промышленности; превосходный старт для дальнейшей карьеры; выпускник, недавний, человечество, технический процесс, что касается (относительно), применение, работа в команде, иметь отношение, производство энергии, осуществлять (приводить в жизнь), поощрять (одобрять). Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations. 1. industrial a. experience 2. key b. skills 3. management c. path 4. consistent d. links 5. case e. knowledge 6. industrial f. demand 7. gain g. placement 8. work h. role 9. increase i. study 10. career j. employability b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) and answer the questions. 1. What _____students’ employability? 2. Does your university have _____ links with regional enterprises? 3. Who influenced your career _____? 4. What professions are always in _____ demand in the modern society? 5. Why is it necessary for students to analyze case _____? 6. Are ______ skills necessary for all specialties? 7. Which companies can students get industrial _____? 8. Does mechanical engineering play a key _____ in industry? 9. What spheres should you _____ knowledge to get a well-paid job? 10. Where can students gain work _____? Exercise 7. Are the statements True or False? 1. The Department of Mechanical Engineering was the top-rated the previous year. 2. Nowadays Mechanical Engineering surrenders the top position. 3. Mechanical engineers need management skills. 4. Mechanical engineering study deal only with engineering. 5. There is a consistent demand for mechanical engineering graduates. 6. During the first and second years of study, students have a mix of lectures, practicals and case studies. 7. Students are not paid for industrial training. 8. The department doesn’t encourage students to gain work experience. 9. The department has a lot of links with employers. 10. On graduation students don’t have challenging opportunities. employment Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. Why is the Department of Mechanical Engineering so popular? 2. Does mechanical engineering play an important role in industry? 3. What do mechanical engineers do? 4. Is it necessary for engineers to be skillful? 5. Do you like to study mechanical engineering? Why? 6. Which subjects do you study? Are there any subjects you would like to drop? 7. Is your course practical? Do you like this way of working? 8. How are you assessed? Do you think this is fair? Exercise 9. Match each engineering branch with one of the processes. 1. Automotive develops a. construction of buildings and engineering infrastructure ranging from skyscrapers and schools to roads and water mains. 2.Civil creates b. the best ways to use electrical power in engineering numerous products, work with electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The primary duties of this profession include designing, developing, testing and overlooking the production or installation of electrical equipment, components and systems. 3. Information finds c. environmental problems and finds technology solutions to issues that affect the engineering environment. 4.Electrical deals with d. software engineering, hardware engineering engineering, integration of hardware and software or validation and verification of hardware and software components. 5.Mechanical manufactures e. generators, turbines, refrigeration engineering equipment, engines, industrial gear, elevators 6.Environmental engineering produces 7. Hydroelectric engineering solves 8. Defense engineering designs f. cars and automobile systems, works on all physical aspects of the car, developing new technologies, improving fuel efficiency and generally making cars safer and more profitable, finds cost-effective materials for building products and identifies ways of improving fuel-system performance. g. and maintains the mechanical technology at hydroelectric plants and oversees the overall performance on the plant. h. technology that is used to ensure national security and maintain the stability of governments and nations throughout the world. Exercise 10. a) Match the verbs with prepositions. 1. take part a. into 2. relate b. on 3. put c. in 4. focus d. on 5. rely e. up 6. give f. on 7. comment g. to b) Translate the sentences using verbs with prepositions from a). 1. Преподаватель попросил студентов сосредоточиться на главной проблеме. 2. Во время стажировки на нашем предприятии вы можете применить свои знания на практике. 3. Мы не можем положиться на результаты одного эксперимента. 4. Старшекурсники принимают участие в междисциплинарных проектах. 5. Студенты хотели выяснить количество экзаменов в летнюю сессию. 6. Нас попросили прокомментировать представленную информацию. 7. Этот вопрос интересный, но он не относится к нашему предмету. Exercise 11. a) Study the course description. Each section begins with a question, as in the examples. Fill in the rest questions. b) With the help of the text, explain these terms. 1 vocationally-focused 2 conventional entry requirements 3 work-based learning 4 prior knowledge 5 in-course assessments 6 sustained growth Computing – Web Technologies Foundation Degree - Level 4 - Part Time 1. What does this course involve? Who is this course for? What are the course aims? This course is a vocationally-focused higher education qualification. It provides the high level of technical skills that will be needed by many organizations. Foundation Degrees are designed for learners from a wide range of backgrounds, including those who have work experience but do not have conventional entry requirements. 2. ________________________ The Foundation Degree in Computing (Web Technologies) will include IT Applications (Access and Excel), System Design, User Support, and Professional Studies. Additional modules enable particular specialisms to be developed. These include Website Development, Visual Programming, Database Systems, Networks and Communications, and Website Management. 3. _______________________ The course is delivered using tutor-led classes, workshops, practical sessions, and tutorials. Additional support is given when requested. 4. _______________________ For the two-year course: students must have at least one year of experience in related employment and an employer who is willing to support them by providing suitable work-based learning projects and academic monitoring. Prior knowledge of computing is helpful but not essential. 5. _______________________ The programme of study requires you to study twelve modules over two or three years. 6. _______________________ Studying over two years requires attendance for one day per week from 9 a.m. till 9 p.m. with breaks. 7. _______________________ All units are assessed and graded. Most units involve in-course assessments. Systems Design and Networks and Communications are assessed by examination. To be awarded a Foundation Degree, you must pass a minimum of ten modules. 8. _______________________ Further study: The Foundation Degree in Computing (Web Technologies) has been designed to enable successful students to progress to the final stage of the University's Honours Degree in Computer Studies should they wish to do so. This would involve just one more year of full-time study or two years of part-time study. A career: A Foundation Degree opens up the possibility of a career in a wide range of areas throughout commerce, industry, entertainment, and the public sector. There is sustained growth in employment prospects for all IT specialists. Exercise 12. Answer the questions about your course and write a leaflet for it. Leaflet – a small book or piece of paper advertising something or giving information on a particular subject 1. Who is the course for? 2. What qualifications do I need? 3. What will I learn on the course? 4. How will I learn? 5. How will I be assessed? 6. What can I do when I finish the course? Exercise 13. Report the following yes/no questions. 1. “Are you involved in this project?” My friend asked me __________________ 2. Do you have hands-on experience in this field?” The employer wanted to know_______________ 3. “Is there a lecture on mechanics today?” My friend wondered__________________ 4. Can we specialize in different subjects?” The students asked the tutor_________ 5. Have you ever been to the lectures of this scientist?” He asked me_____________________ 6. “Did the company pay for our training?” The engineer asked________________ 7. “Is he working on the report for his thesis?” She found out_____________________ 8. “Does taking English earn credits to the degree?” The student asked__________________ Exercise 14. Report the following questions. 1. What does the undergraduate engineering program include? (applicants wanted to know) 2. Where did you acquire such management skills? (the employer wondered) 3. What subjects will be taught next year? (students asked) 4. What are the formal education requirements for engineers? (the tutor explained) 5. How many exams will we take this term? (I forgot) 6. Why haven’t you shifted to the company with better prospects? (the manager inquired) 7. Where can electronic engineers work? (the supervisor explained) 8. How long does it take to get profound knowledge in this field? (she asked) Exercise 15. In each of the following sentences there is a mistake. Find it and correct it. 1. Students asked if there is a consistent demand for the graduates of the university. 2. My friend was wondering that I was interested in doing research. 3. The manager had no idea whether had our design team won a grant for innovative technology. 4. The teacher said to apprentices if they were looking forward to obtaining vocational qualifications. 5. The inspector wanted to know if do the third year students gain specialist knowledge. 6. They were wondering whether the programme of study requires students to study several modules. 7. They tried to find out if students are given additional support when requested. 8. School leavers were eager to know if industrial experience did increase motivation to succeed in chosen profession. Exercise 16. Watch a video “McMaster Engineering: Department of Mechanical Engineering” “https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tLFqZZehKGo and find out the following: 1. industries where mechanical engineering students can work 2. transferable skills students can obtain 3. the importance of working in a team. Exercise 17. Refer to the site of your department and write a review on the following: general information about the department, teaching staff, its specialties, your own area of study, characteristics, curriculum, future job opportunities, additional education opportunities. Get ready with the presentation “The Importance of Engineering Education” Consider the following points: - where you can get engineering education; - the specialist knowledge required; - how long it takes to get profound knowledge; - the necessary skills needed; - if work experience increases employability; - career opportunities. E. EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS FOR ENGINEERS Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. a) What makes a successful engineer? Here are some things, which could be important. Rank them from 1 to 7. Explain your choices. education impersonal skills hands-on experience management skills on-going training communication skills personal traits b) What other things do you think are important for a successful engineer? Exercise 2. Match the words (1-10) with their meaning (a-j) 1. curriculum a. experience gained from doing a job rather than studying it 2. related branch b. people’s characteristic patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors 3. hands-on experience c. branch belonging to the same family, group, or type 4. profound d. relating to the special skills, training, that you need for a particular job or occupation 5. in short supply e. the subjects comprising a course of study in a college or university 6. crucial f. not easily obtainable; scarce 7. vocational g. a thing that must be seen or done, it is absolutely necessary 8. executive h. of great importance 9. personal traits i. showing great intellectual depth and understanding 10. must j. a person with senior managerial responsibility in a business Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps using the words from Exercise 2. 1. _____are given a lot of powers. 2. Engineers can work in _____. 3. Time management skills are a _____ in this profession. 4. Many subjects are included in the university _____. 5. We stopped at the nearest gas station because petrol was _____. 6. _____ may influence the choice of the career. 7. Apprenticeships help students gain _____. 8. Our course is designed to provide _____ training in engineering. 9. He took all _____ decisions all by himself. 10. The university course provides students with _____ theoretical knowledge. Exercise 4. Read the text and say what is necessary to succeed in the engineer career. Education Requirements for Engineers Engineer is a most sought-after profession in the modern world because of the ongoing development of industry and new technologies. Engineering occupations are found in many fields such as electric and heat power engineering, mechanical engineering, electronics, power engineering, metallurgy, IT technology, civil engineering, etc. Engineers transform scientific discoveries into commercial applications that help consumers and society in general. Russian engineering universities offer high-level education, which attracts applicants from all over the world. They gain profound theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience. A four-year bachelor’s degree in engineering is required for most entry-level engineering positions. The undergraduate engineering program typically includes coursework in general engineering along with courses in math, physical and life science. In a typical 4-year curriculum, the first 2 years are spent studying mathematics, basic sciences, introductory engineering, humanities, and social sciences. In the last 2 years, most courses are in engineering, usually with a concentration in one branch. The curriculum also incorporates the basics of other engineering disciplines, such as chemical, electrical and civil engineering. Typical studies include calculus, thermodynamics, physics, materials science, statics, dynamics and fluid dynamics, and laboratory sections. Engineers trained in one branch may work in related branches. This flexibility allows employers to meet staffing needs in new technologies and specialties in which engineers may be in short supply. It also allows engineers to shift to fields with better employment prospects or to those that more closely match their interests. If you want to do research in any of areas, or make new findings, you need a Master's and a PhD. Ongoing training is crucial for engineers, especially those who wish to advance in the field. An advanced degree such as a master’s in engineering is usually required for those who want to pursue advanced research and development positions. Apart from the formal education requirements, engineers also need hands-on experience that includes practical problem solving. Vocational schemes and apprenticeships can help you gain this experience. Many engineers obtain graduate degrees in engineering or business administration to learn new technology and broaden their education. Many high-level executives in government and industry began their careers as engineers. While engineering education provides the foundation needed to land a job, there are a few personal traits as well as educational requirements you should have to succeed in this work field. These traits include good analytical and problem solving skills, creativity, and designing innovation, the ability to adapt quickly to any changes, and extreme focus and determination. Engineers should be detail-oriented, systematic and highly computer-literate. Additionally, many employers require engineers to demonstrate effective interpersonal and time management skills, as they work with teams on specific projects. Spoken and written skills are also must, as this career requires you to communicate findings, present recommendation and discuss issues. These traits will help you since engineering is a difficult job both onsite and in the office. These are just the bare minimum requirements for engineering, and it is always better to gain as much work experience as possible after graduation. The more experience you gain, the better off you will be, and the more you will be able to succeed in this fast paced, ever changing career. Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Пользующийся спросом, применение, включать, работодатель, совершенствоваться, кроме, преуспевать, добиваться определенного общественного положения, получить работу, решительность (решимость), ориентированный на изучение деталей, умеющий пользоваться компьютером, дополнительно, навыки межличностных отношений, обсуждать проблемы, абсолютный минимум, динамичный Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations 1. to gain a. one’s education 2. employment b. profession 3. to match c. skills 4. to pursue d. issues 5. to land 6. to demonstrate 7. sought-after 8. ongoing 9. to broaden 10. to discuss e. knowledge f. one’s interest g. development h. prospects i. a job j. training b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) in the correct form and answer the questions. 1. What _____ professions in the modern world can you think of? 2. What personal traits are needed _____ an engineer’s job? 3. What knowledge is necessary to_____ for engineering jobs? 4. What skills should engineers _____ to meet employers’ requirements? 5. Does your future job _____ your interests? 6. What skills are required in discussing _____? 7. Which jobs is _____ training important for? 8. Do you plan to obtain graduate degree _____ your education? 9. Do qualified specialists have more _____ prospects? 10. Would you like _____ development position after graduating from the university? Exercise 7. Are the statements True or False? 1. Nobody wants to enter Russian engineering universities. 2. Entry-level engineering positions require five years. 3. The curriculum incorporates many subjects. 4. Engineers are trained only for one branch. 5. If you wish to advance you need ongoing training. 6. Apprenticeships can help you gain hands-on experience. 7. Many CEOs began their careers as engineers. 8. To succeed in the job you should possess some personal traits. 9. Engineers work onsite and in offices. 10. The more knowledge and experience you gain the better. Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. Why is an engineer a demanding profession nowadays? 2. In which way do engineers help consumers and society? 3. What does an entry-level engineering position require? 4. What disciplines does the curriculum incorporate? 5. Where can engineers work? 6. When is an advanced degree necessary? 7. How can you gain hands-on experience? 8. What personal traits are necessary to land an engineer’s job and to succeed in engineering? Exercise 9. In each of the following sentences there is a mistake. Find it and correct it. 1. If you doesn’t give up learning, you will never cease to grow. 2. You wouldn’t pass your exams if you didn’t revised. 3. If you was a student of the liberal-art college you would have opportunities to choose more electives than do students of technical schools. 4. Could they look through this article we will discuss it. 5. A degree or certificate from a college or university will be useless if employers or other institutions had not recognized it. 6. The tutor would help you if you had asked him to. 7. If his college established affiliation with employers and researchers, he would have obtained hands-on and invaluable experience. Exercise 10. Personal traits include different skills, which can influence your career. Match the skills with the description. 1. analytical skills a. the generation of new ideas or concepts, or new associations between existing ideas or concepts, and their substantiation into a product that has novelty and originality. 2. problem-solving skills b. getting your written message across clearly, concisely and effectively. 3. creativity c. collecting data, performing all sorts of analyses, and arriving at meaningful conclusions, detecting patterns, brainstorming, observing, interpreting data, integrating new information, theorizing. 4. detail-oriented d. the process of planning and exercising conscious control of time spent on 5. interpersonal skills 6. time management skills 7. spoken skills 8. written skills specific activities, especially to increase effectiveness, efficiency, and productivity. e. the tendency to be accurate and thorough; usually related to catching and/or avoiding mistakes or to improving a system or experience. f. determining the source of a problem and find an effective solution. g. effectively addressing an audience whether it is in front of a group of people you already know or a crowd of complete strangers, your ability to communicate to them with clarity and confidence. h. qualities and behaviors we exhibit while interacting with other people. A key indicator of success in a working environment, as benefits include the ability to cooperate with teammates to solve difficult problems, as well as simply enhancing your popularity around the office. Exercise 11. a) Match the verbs with prepositions 1. cooperate a. into 2. work b. for 3. transform c. in 4. train d. through 5. research e. with 6. succeed f. in 7. get g. for 8. require h. on b) Translate the sentences using verbs with prepositions from a). 1. Наш университет готовит специалистов для всех отраслей промышленности. 2. В настоящее время наш отдел работает над новым проектом. 3. Студенты проводят исследования во многих отраслях. 4. Сотрудники нашего отдела превращают научные разработки в коммерческие проекты. 5. Она с легкостью сдала свой последний экзамен. 6. Инженеры должны взаимодействовать с командой для решения сложных задач. 7. Хорошее образование поможет вам добиться успеха в жизни. 8. Степень бакалавра требуется для многих инженерных должностей. Exercise 12. Read an extract from a job description for an electronic engineer and write requirements for your future profession. Electronic engineers are highly sought after, well rewarded and can be found in practically every branch of industry and commerce. Scope and responsibilities The Senior Electronics Design Engineer will be responsible for enhancing and supporting the entire electronic design process, including, but not limited to: - electronic product development from design to production release - electronic design, analysis and testing of new products from product specification, producing electronic prototypes and preparation of all necessary design documentation - firmware design for electronic devices - electronic circuit design and board layout for very small devices and instruments - accurate project and design documentation - interfacing closely with marketing to create and develop products according to customer needs - interacting with contract engineers that support product development - developing and maintaining vendor selection and involvement to ensure the highest quality products - obtaining necessary product approvals and communicating progress throughout the design process - providing technical support for new and existing products in manufacturing and in the field - producing design schedules - staffing and operating an electronics lab Exercise 13. Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first sentence using the word given. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given. 1. I have too much work to do so I can't go out with you tonight. only If _____so much work, I could go out with you tonight. 2. They ought to tell us what the new timetable is. about It _____us what the new timetable is. 3. Please don't copy my answers! rather I _____copy my answers! 4. She needs to get a scholarship in order to go to that college. if She could go to that college _____a scholarship. 5. I don't like living so far from the university. closer I wish _____ college. 6. I regret not buying that book you recommended. only If _____that book you recommended. 7. You don't pay enough attention in class. wish I _____ attention in class. 8. You'd better start revising for the exam! time It's _____revising for the exam. 9. Maybe my dream will come true and I'll go to Cambridge! if What _____ true and I went to Cambridge! 10. I think you should do your homework on your own from now on. high It _____your homework on your own. Exercise 14. Use the correct tense of the verb. 1. If you _____ (want) to do research in any of areas, or make new findings, you will need a Master's and a PhD because ongoing training is crucial for engineers. 2. You _____ (live) close to campus with your family, if the college system utilized credit units. 3. If students live and pay taxes in the particular US state, they _____ (pay) lower tuition than out-of-state residents do. 4. The UK universities _____ (offer) bursaries, if students are eligible for financial help. 5. If the exchange program _____ (be) in an overseas institution, students would get the benefit of experiencing life in a different country, living in a different culture or among several cultures, learning a foreign language. 6. Engineers would have obtained graduate degrees, if they _____ (want) to learn new technology and broaden their education. 7. You _____ (get) a place at the UK University, if you had good A-level results in at least two subjects. Exercise 15. Watch a video “Raise the Bar for Engineering” - Extended Version https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JukurryDh74 and match the speaker and his/her words. 1. Wayne Clough, PhD, PE a. We need to change licensing requirements and raise the bar because the challenges that engineers face today are so much more complex than they have been in the past. 2. Norman Augustine, PE b. More and more engineers are looking for additional class work looking for the master’s degree. 3. Christine Andersen, PE c. You really have to redesign the entire process. 4. Jennifer Epp, PE 5. Ken Fridley, PhD, PE d. It’s at the public’s interest that we make the master’s degree the basic theory of the engineering profession. e. The public expectation as well as employer expectations are much broader and deeper for the engineering graduates today. Exercise 16. Refer to the sites www.careerprofiles.info, www.prospects.ac.uk, find three or four possible professions in your field and summarize education requirements to get the position. F. RUSSIAN NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS Exercise 1. Connect with the topic. - What do you know about Alfred Nobel? - What do you know about the Nobel Prize? - How often are the prizes awarded? - Which nominations are there? - When did the award start? - Who was the first Russian Nobel prizewinner? - What is the most often awarded prize for Russians? Exercise 2. Match the words with their meaning 1. recognized a. the physics of atomic nuclei and their interactions 2. to train b. to cause something to happen or exist, to produce as an effect 3. discovery c. to complete a course at a university 4. contribution d. finding something 5. to result in e. a solid substance that has a conductivity between that of an insulator and that of most metals 6. nuclear physics f. notable, distinguished, honored 7. to influence g. to have an effect on behaviour or situation 8. violence h. to teach a person to do something which is difficult or needs practice 9. graduate from i. something that you give or do together with others 10. semiconductor j. behavior which is intended to hurt, injure, or kill people Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps using the words from Exercise 2. 1. The 20th century is known for world-shaking _____. 2. _____ are widely used in electrical engineering. 3. Who _____ the choice of your career? 4. It is better to buy goods from a _____ dealer. 5. This scientist is known for his _____ research. 6. The university _____ qualified specialists. 7. Global warming _____ disastrous ecological changes. 8. The government used _____ to break up the demonstration. 9. Andrei Sakharov was awarded a prize for his _____ to world peace. 10. Bill Gates _____ Harvard University. Exercise 4. On the basis of the text complete the table. Use the Internet sources and add three more Nobel Prize winners. Name Date Discovery Co-winners Russian Nobel Prize Winners in Physics and Chemistry Because of its long history of supporting scientific research and education, Russia has produced a number of internationally recognized leaders in physics and chemistry. The Russian Academy of Sciences (or the USSR Academy of Sciences, as it was called before 1991), played a major part in all their careers. With one exception, all were members of the Academy, carrying out their research and publishing their finding with the Academy’s support. Semyonov N.N. In 1956, Nikolay N. Semyonov was 1st Russian to receive a Nobel Prize for Chemistry for his research into the mechanism of chemical reactions. He was trained as a physicist and chemist. During his career, working alone or with other distinguished scientists like Pyotr L. Kapitsa, he made many important discoveries and contributions to chemistry and physics. In 1931, Semyonov became the first director of the Institute of Chemical Physics of the Academy and was also one of the founders of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT). Cherenkov P.A. Tamm I.Y. Frank I.M. The collaboration of Pavel A. Cherenkov, Igor Y. Tamm and Ilya M. Frank resulted in the discovery and description of the Cherenkov – Vavilov effect, a phenomenon which is very important in nuclear physics. For their work they received the Nobel Prize in 1958. All three of the scientists were professors at universities and the Academy’s institutes and greatly influenced future generations of scientists. Landau L.D. After receiving his doctoral degree from Leningrad University at the exceptionally young age of 19, Lev D. Landau went on to study abroad. When he returned to Russia, he became head of two of the Academy’s institutes. Like Semyonov, he was also involved in founding the MIPT. He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1962, for his phenomenological theory of superfluidity in helium. Basov N.G. Prokhorov A.M. Nikolay G. Basov and Aleksandr M. Prokhorov worked together on a project which led to the development of the laser and their receiving the 1964 Nobel Prize. Both worked at the Lebedev Institute of Physics (Basov was the Director from 19731988) and also taught at universities. Even though Prokhorov never became a member of the Academy, the Academy’s General Physics Institute was renamed after the A. M. Prokhorov General Physics Institute in his honour. Kapitsa P.L. Pyotr L. Kapitsa went to England after he had completed his studies at Petrograd Polytechnic Institute. He studied at Cambridge and also worked on various projects there. He returned to Russia in 1934 and continued his career there. He was also one of the founders of the MIPT. In addition, Kapitsa was a member of the Soviet National Committee of the Pugwash movement, a group of international scientists who wanted to use science for the good of humankind and not for violence and war. Kapitsa won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1978, for his work on low-temperature physics. Alferov Z.I. Zhores I. Alferov has been active in physics since graduating from the Electrotechnical Institute in Leningrad. He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 2000, for the development of the semiconductor heterostructures used in high-speed electronics and optoelectronics. Ginsburg V.L. Abrikosov A.A. More recently, Russian Nobel Prize winners in 2003 were Vitaly L. Ginsburg and Alexei A. Abrikosov. Ginsburg, who holds a doctoral degree from Moscow State University, became the director of the Academy’s Physics Institute after Igor Tamm. Ginsburg was influenced by Landau, with whom he had worked, and by Tamm, who had been his teacher. Alexei Abrikosov was educated at Moscow State University. He worked at the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics for over 20 years (1965-1988) and also taught at Moscow State University during that time. They received the Nobel Prize for Physics for pioneering contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids. Exercise 5. Find in the text English equivalents to the following words and word combinations. Исключение; вести исследования; публиковать новости об открытиях; получить нобелевский приз; делать важные открытия; основатели университета; описывать что-либо; докторская степень; закончить обучение; развитие чеголибо; теория о; работать над проектом; стать главой чего-либо; различные виды работ; быть переименованным, основная часть, за исключением, поддержка, вклад, сотрудничество, описание, поколение, включать (вовлекать), назвать в честь кого-либо, завершать, высокоскоростной Exercise 6. a) Match the words to get word combinations. 1. scientific a. degree 2. recognized b. physics 3. doctoral 4.study 5. theoretical 6. receive 7. chemical 8. major c. prize d. research e. reaction f. leader g. part h. abroad b) Fill in the gaps using the words from a) and answer the questions. 1. How do you spend the major _____ of your time? 2. What is necessary for receiving the _____ degree? 3. Does your university provide laboratories to carry out _____ reactions? 4. What course do students study theoretical _____ at? 5. Where can students conduct their _____ research? 6. Have you _____ any prizes? 7. Would you like to take a gap year to study _____? 8. What _____ leaders in your specialty can you name? Exercise 7. Are the statements True or False? 1. All Russian Nobel prizewinners were members of the Russian Academy of Sciences. 2. N. N. Semyonov was the first Russian to receive a Nobel Prize for Chemistry. 3. The Cherenkov–Vavilov effect is very important in theoretical physics. 4. Pavel A. Cherenkov, Igor Y. Tamm and Ilya M. Frank have no influence on other scientists. 5. Lev D. Landau received his doctoral degree abroad. 6. Nikolay G. Basov and Aleksandr M. Prokhorov shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1964. 7. Pyotr L. Kapitsa was a member of the Soviet National Committee of the Pugwash movement. 8. Zhores I. Alferov got high education in Moscow. 9. Tamm was Ginsburg’s teacher. 10. Vitaly L. Ginsburg and Alexei A. Abrikosov received the Nobel Prize for Physics for contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids. Exercise 8. Answer the questions using the information from the text. 1. Do you think it is a good idea to award prizes to scientists for their work? Why? 2. How many Nobel Prize winners were members of the Academy? 3. Which scientists were among those who founded the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology? 4. Which scientists, apart from Lev Landau, had things or places named after them? 5. Which scientists left the country to further their studies? 6. Who was the director of the Academy’s Physics Institute before Vitaly Ginsburg? 7. What does the Nobel Prize represent? 8. Why do you think it’s such a prestigious award? Exercise 9. a) Match the verbs with prepositions. 1. carry a. from 2. result b. in 3. involve c. down 4. write d. on 5. lead e. out 6. work f. in 7. graduate g. to b) Translate the sentences using verbs with prepositions from a) 1. Разработки ученых привели к новым открытиям. 2. Ученый тщательно записывал результаты всех своих опытов. 3. Студенты проводят опыты в хорошо оснащенных лабораториях. 4. Мы закончим университет и станем квалифицированными специалистами. 5. Многие студенты участвуют в научных конференциях. 6. Авария привела к катастрофическим экологическим изменениям. 7. В данный момент специалисты работают над этой проблемой. Exercise 10. Use a word in the correct form in each gap to complete the text. hesitation reflection image comprehend recall genius train Big Brains Many of the world’s _____ (1) have described how they think. They often think in the same way, and it may be that they have a different way of _____ (2) the world to the rest of us. For one thing, they rely often on mental _____ (3) of things to help them remember things rather than on _____ (4) actual language. This is something that all of us can actually _____ (5) ourselves to do better. They also report to take more time for _____ (6); that is, they _____ (7) before they speak because they want to give themselves more time to express themselves accurately. Exercise 11. Complete the text with the right word. Alfred Nobel When we hear the name Nobel, we immediately think of the Nobel Prizes. But Alfred Nobel, the 1) _____ (holder/creator/discoverer/receiver) of the awards, was also a great 2) _____ (scientist/engine/philosophy/production) and 3) _____ direction/invention/maker/inventor). Born in 1933 in Sweden, Nobel studied first in Russia and then 4) _____ (transferred/visited/joined/emigrated) to the US where he studied mechanical 5) _____ (developing/producing/engineering/creating). Afterwards, he returned to Sweden to work with his father. Gradually, they made 6) _____ (directions/advances/motions/movements) in explosives. Nobel 7) _____ (figured/solved/granted/introduced) out how to work safely with nitroglycerine, a very dangerous and explosive 8) _____ (shape/form/body/substance). His invention later became known 9) _____ (by/with/as/for) dynamite. Nobel continued throughout his life to 10) _____ (do/have/make/take) improvements in the field of explosives. He eventually owned 11) _____ (numerous/numerate/numerical/numbered) explosives factories around the world and became very wealthy. Alfred Nobel was a man of great 12) _____ (advantage/achievement/situation/incident). When he died, he left a wonderful gift to the world: the Nobel Prizes. Each year these prizes are 13) _____ (awarded/designed/suggested/implanted) to scientists, inventors and other 14) _____ (developed/interested/creative/manageable) people for their great 15) _____ (involvement/contribution/manufacturing/development) to the world. Exercise 12. Match two parts to form conditional sentences and translate them. 1. If the significance of the achievement has a. prizes will be withheld or not withstood the test of time awarded. 2. If the person confers the greatest benefit to b. the award will be divided mankind equally between the recipients. 3. If there are 2 or 3 laureates in a particular c. he/she will be required to give a category public lecture on a subject related to the topic of the prize. 4. If a prize is declined or not accepted before d. the scientist will be awarded the a set date Nobel Prize. 5. If the refuser has later explained the situation e. he would not have changed his and on application received the Nobel gold will. medal and the diploma 6. If no candidate in the meaning of Nobel’s f. he/she will receive the Nobel will are found or the world situation prevents Prize. gathering information required to reach a decision 7. If a person supplies a self-nomination for the g. it will go to benefit scientific, Nobel Prize cultural or humanitarian causes. 8. If Alfred Nobel had not read his own h. the prize money will go back to obituary “The merchant of death is dead” the funds. 9. If the Nobel Prize in Chemistry had not been i. the nominee will be awarded to non-chemists (biochemistry, automatically disqualified. molecular biology) 10. If the winners donate the prize money j. the money will revert to the funds. 11. If a laureate is awarded the Nobel Prize k. it would not have been criticized. Exercise 13. Use the correct tense of the verb to make the first, second and third conditionals. Use adverbs of time where it is necessary. 1. If you _____ (take) the undergraduate engineering program, the coursework _____ (include) general engineering and courses in math, physical and life science. 2. He _____ (start) work as a technician or go on to further study at university, if he _____ (graduate) from this college 3. Students _____ (obtain) proficiency, if they _____ (use) the latest technologies in their study. 4. If she _____ (be) a student of a technical or vocational college, it _____ (train) her in the theory behind a specific vocation or technology. 5. Vocational schemes _____ (help) you, if you _____ (want) to gain hands-on experience. 6. If my friend _____(choose) an apprenticeship, he _____ (start) work and earn money as soon as possible. 7. If students _____ (study) communications skills, it _____ (help) them deal with communication at work and with public. Exercise 14. Watch a video “Top 10 Nobel Prize Winners”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ia4h_qRjxX0 and list Nobel Prizewinners and their achievements. Get ready with the presentation “Nobel Prize Winners from other Countries in your Sphere of Knowledge”. Consider the following points: - the founder of the prize; - the short information about the prize; - the countries the most often awarded scientists are from; - the Nobel Prize winners in your sphere of knowledge; - what discoveries/contributions they were awarded for.