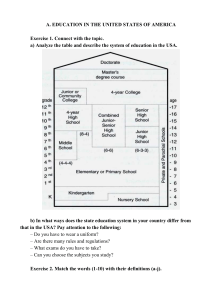
Higher Education in Russia 1 Vocabulary 1. Give Russian equivalents to these expressions competitive examination with merit and credit applicants take notes borrow books from the university library computerassisted learning materials to present a graduation thesis to be transferred to the next course sciences and humanities well grounded in a specific field of engineering optional courses obligatory subjects self-study to be engaged in research Post-graduate education under the guidance and supervision highly qualified specialists strength of materials to read for credit tests and exams housing construction 2. Practice using the following vocabulary What do we call: 1) a person who takes an examination in order to enter a University? 2) a first year student? 3) a person who studies at a higher educational Institution? 4) a student in his final year of studies? We call him (her): a candidate or an applicant. a freshman or a fresher. an undergraduate. a graduate. a resident student; a 5) a student who lives (doesn’t live) in the hostel? day student. 6) a student who combines (doesn’t combine) work with a part-time student; a study? full-time student. 7) a graduate who continues his studies to receive a a postgraduate. degree? 8) a student (graduate) who had been given his first a Bachelor of Arts. degree? 9) a student who studies at the Extramural Department? an external student. What do we call a room: We call it: 1) where meetings, conferences and parties are held? an assembly-hall. 2) which is used for gymnastics? a gymnasium (gym). 3) which is used by the teaching-staff for work and rest a staff common room. during the breaks? 4) which is used as a place of business where students’ progress, attendance and testing of knowledge are given the Dean’s office. day-by-day guidance? 3. Practise using prepositions A) I went in for I sat for I took I had I did well I did well I passed my examination I got through I failed my examination in Mathematics in Physics in in Economics in History in spring. English at (in) the English examination in Physics in Mathematics - with merit. with credit. satisfactory. - in History in (at) my examination in miserably. English. Reading 1. Read the text and choose headings to each of the 5 parts of it from the box a) Research at a university. b) Course of training. c) Specialization of universities. d) Organization of studies. e) Entrance to universities. 1. Entrance to universities is by competitive examination or by the results of the Unified State Exam which is open to anyone between the age 17 and 35 having secondary education. Those who passed entrance examinations with merit and credit receive monthly financial support in the form of state grants. Students pay nothing for lectures and for using the laboratory equipment. If the applicants did not fail in the examinations but their results are satisfactory they can gain entrance but must pay for their education. 2. The complete course at the university lasts for 5 years, in some educational establishments it may be a little longer or shorter. Students have lectures and practical hours. They attend lectures on different subjects: Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Philosophy, History of Russia, Economics, Strength of Materials, Drawing and others and take notes of them. Studying at the university is a great experience for students because theoretical material is always supported by practical exercises. During practical hours in the laboratories and shops they study the material of the lectures. Students can borrow books from the university library and use computer-assisted learning materials to read for credit tests and exams. The academic year is divided into two terms from September to January and from February to July. Students take examinations at the end of a term and can be transferred to the next course. On completion of studies the student passes final state examinations and presents a graduation thesis. 3. The classic universities train highly qualified specialists in sciences and humanities. The specialized universities train specialists for one of the fields of culture or national economy. The graduates of specialized technical universities are well grounded in a specific field of engineering. Special attention is given to the training of technical engineering personnel in most important branches of modern transport, industrial and housing construction. In all higher educational institutions there are some optional courses which provide students with an opportunity to study besides obligatory subjects, subjects they are most interested in. 5. Besides full-time education many institutions offer evening and correspondence teaching. The curricular of correspondence and evening higher schools do not differ essentially in the subjects taught, but they differ in the system in which studies are organized. The basic form of study has tendered to give a high priority to independent work and self-study at home. The majority of evening and correspondence students study professions they are engaged in. 6. Those who have a gift for research work may take advanced exams in philosophy, foreign language and a certain field of knowledge to enter the post graduate course. A postgraduate carries out his research and works at the doctoral thesis under the guidance and supervision of the experienced professors and academics. They should work hard to get the highest academic qualification. Answer the questions. 1. Do students have to pay for their education? 2. Do students get grants for further education? 3. How long does the course of studies at the university usually last? 4. How many terms are there in the academic year? 5. Where do students take textbooks? Do they usually buy them? 6*. What can you say about the trends in Russian educational system? Is it concentrating more on purely academic subjects or on more practical ones? 7*. Would you say that people in Russia are more or less enthusiastic about university education than they are in Britain? 8*. What would you say are the successes and failures of Russian educational systems? Compare British and Russian educational systems.