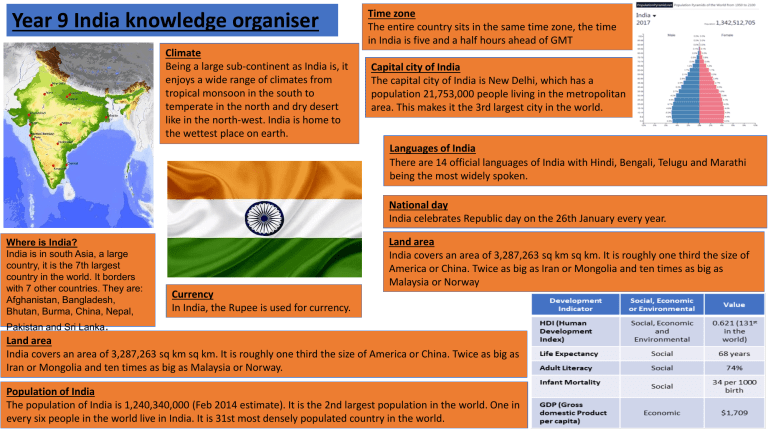
Year 9 India knowledge organiser Climate Being a large sub-continent as India is, it enjoys a wide range of climates from tropical monsoon in the south to temperate in the north and dry desert like in the north-west. India is home to the wettest place on earth. Time zone The entire country sits in the same time zone, the time in India is five and a half hours ahead of GMT Capital city of India The capital city of India is New Delhi, which has a population 21,753,000 people living in the metropolitan area. This makes it the 3rd largest city in the world. Languages of India There are 14 official languages of India with Hindi, Bengali, Telugu and Marathi being the most widely spoken. National day India celebrates Republic day on the 26th January every year. Where is India? India is in south Asia, a large country, it is the 7th largest country in the world. It borders with 7 other countries. They are: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Burma, China, Nepal, Land area India covers an area of 3,287,263 sq km sq km. It is roughly one third the size of America or China. Twice as big as Iran or Mongolia and ten times as big as Malaysia or Norway Currency In India, the Rupee is used for currency. Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Land area India covers an area of 3,287,263 sq km sq km. It is roughly one third the size of America or China. Twice as big as Iran or Mongolia and ten times as big as Malaysia or Norway. Population of India The population of India is 1,240,340,000 (Feb 2014 estimate). It is the 2nd largest population in the world. One in every six people in the world live in India. It is 31st most densely populated country in the world. Geopolitics Definition: How are a countries world politics influenced by geographical factors. Globally: India is a member of the G20. The G20 are the twenty most developed economies in the world. These countries meet every year, and discuss world trade issues Impact on the environment India is ranked as the 155th country out of 177 in a global ranking on environmental quality. This costs India around $80 billion per year (5.7% of its total economy) Impact of Development The Elderly (50+): Access to better healthcare, which may prolong their life. Do not possess necessary skills so may lag behind. Socially, changes to the Indian society may be difficult to adapt to. Females: The BIGGEST winners: Emancipation of women = equal access to a high quality education and healthcare system, which enables them access to highly skilled jobs that are well paid. Solid Waste Pollution: Indian cities generate 100 million tonnes of waste each year. 40% of urban waste in India is just simply not collected, and is allowed to rot on the streets. Water Pollution: India has the capacity the deal with just 1/6 of its sanitation produced. Over 100 Indian cities directly dump untreated sewage into the Ganges. In Asia: The partitioning of India and Pakistan in 1947 was accompanied with riots and mass casualties. The effects of this are still felt today: The relationship between India and Pakistan is still far from healthy Both countries are nuclear armed. Air Pollution: Major issue in India, with wood burning and vehicle emissions behind the primary cause. Natural methods of fuel production (wood burning) constitutes 90% of rural energy, and 24% of urban energy. These biomass house burners are the leading cause of greenhouse gas emissions. Rate of change in female literacy rates (11.8%) greater than males (6.8%) between 2001-2011. Young adults: Access top universities, receiving a world class education = compete for the highest skilled and paid jobs = more equal society.