й з ш с д ьыж ½ • ц жр п я ь с × • кс ь я ж р кне
реклама
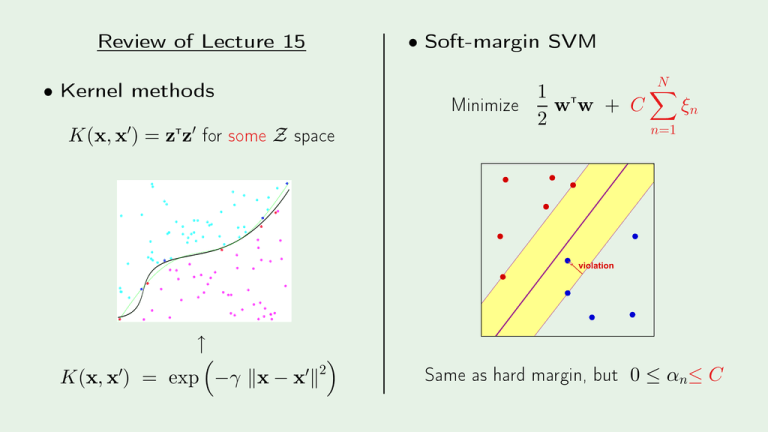
Review of Leture 15
•
Kernel methods
K(x, x′) = zTz′
for some
•
Soft-margin SVM
Minimize
Z
1 T
ww + C
2
spae
N
X
ξn
n=1
Hi
Hi
violation
Hi
↑
K(x, x′) = exp −γ kx − x′k2
Hi
Same as hard margin, but
0 ≤ αn ≤ C
Learning From Data
Yaser S. Abu-Mostafa
California Institute of Tehnology
Leture 16:
Radial Basis Funtions
Sponsored by Calteh's Provost Oe, E&AS Division, and IST
•
Thursday, May 24, 2012
Outline
•
RBF and nearest neighbors
•
RBF and neural networks
•
RBF and kernel methods
•
RBF and regularization
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
2/20
Basi RBF model
Eah
(xn, yn) ∈ D
inuenes
h(x)
based on
radial
Standard form:
h(x) =
N
X
n=1
AM
L
kx
−
x
k
n
| {z }
wn exp −γ kx − xnk2
|
{z
}
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
basis funtion
3/20
The learning algorithm
Finding
w1, · · · , wN :
h(x) =
N
X
n=1
2
wn exp −γ kx − xnk
based on
E = 0:
in
N
X
m=1
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
wm
D = (x1, y1), · · · , (xN , yN )
h(xn) = yn
for
n = 1, · · · , N :
2
exp −γ kxn − xmk = yn
4/20
The solution
N
X
wm exp −γ kxn − xmk
m=1
2
exp(−γ kx1 − x1k )
2
exp(−γ kx2 − x1k )
...
2
exp(−γ kxN − x1k )
|
If
AM
L
Φ
is invertible,
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
...
...
...
...
{z
Φ
2
= yn
N
equations in
2
exp(−γ kx1 − xN k )
2
exp(−γ kx2 − xN k )
...
2
exp(−γ kxN − xN k )
}|
w = Φ−1y
N
unknowns
w1
w2
=
...
wN
{z }
w
y1
y2
..
.
yN
| {z }
y
exat interpolation
5/20
The eet of
h(x) =
N
X
n=1
small
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
γ
γ
wn exp −γ kx − xnk2
large
γ
6/20
RBF for lassiation
h(x) = sign
N
X
n=1
wn exp −γ kx − xnk2
Learning:
s =
∼ linear
N
X
regression for lassiation
wn exp −γ kx − xnk2
n=1
Minimize
!
(s − y)2
on
D
y = ±1
h(x) = sign(s)
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
7/20
Relationship to nearest-neighbor method
Adopt the
AM
L
y
value of a nearby point:
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
similar eet by a basis funtion:
8/20
RBF with
N
parameters
Use
K≪N
w1, · · · , wN
enters:
based on
µ1, · · · , µK
N
K
enters
data points
instead of
x1, · · · , xN
h(x) =
K
X
k=1
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
2
wk exp −γ kx − µk k
1.
How to hoose the enters
µk
2.
How to hoose the weights
wk
9/20
Choosing the enters
Minimize the distane between
xn
and the
losest
Split
enter
µk
x1, · · · , xN
Minimize
:
K -means lustering
into lusters
K
X
X
kxn − µk k
S1, · · · , SK
2
k=1 xn∈Sk
Unsupervised learning
NP -hard
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
10/20
An iterative algorithm
Lloyd's algorithm:
Iteratively minimize
K X
X
kxn − µk k2
w.r.t.
µk , Sk
k=1 xn∈Sk
1 X
xn
µk ←
|Sk |
xn∈Sk
Sk ← {xn : kxn − µk k ≤
Convergene
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
−→
all
kxn − µℓk}
loal minimum
11/20
Lloyd's algorithm in ation
Hi
1. Get the data points
2. Only the inputs!
3. Initialize the enters
4. Iterate
5. These are your
µk 's
Hi
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
12/20
Centers versus support vetors
Hi
support vetors
Hi
Hi
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
RBF enters
Hi
13/20
Choosing the weights
K
X
k=1
wk exp −γ kxn − µk k2 ≈ yn
2
exp(−γ kx1 − µ1k )
2
exp(−γ
kx
−
µ
k
2
1 )
...
2
exp(−γ kxN − µ1k )
|
If
AM
L
ΦT Φ
is invertible,
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
...
...
...
...
{z
Φ
N
equations in
2
K< N
exp(−γ kx1 − µK k )
2
exp(−γ kx2 − µK k )
...
2
exp(−γ kxN − µK k )
}|
w = (ΦTΦ)−1ΦTy
unknowns
w1
w2
≈
...
wK
{z } |
w
y1
y2
...
yN
{z }
y
pseudo-inverse
14/20
RBF network
The features are
exp −γ kx − µk k2
Nonlinear transform depends on
=⇒
D
No longer a linear model
h(x)
b −→ ↑
w1
φ
wk
···
kx − µ1k
φ
kx − µk k
wK
···
φ
kx − µK k
x
b
A bias term (
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
or
w0)
is often added
15/20
Compare to neural networks
w1
φ
h(x)
↑
↑
···
φ
kx − µk k
w1
wK
wk
kx − µ1k
AM
L
h(x)
···
φ
kx − µK k
wk
···
θ
w1Tx
θ
wkT x
wK
···
T x
wK
x
x
RBF network
neural network
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
θ
16/20
Choosing
Treating
γ
as a parameter to be learned
γ
h(x) =
K
X
wk exp −γ kx − µk k
k=1
∼ EM
Iterative approah (
algorithm
in mixture of Gaussians):
1.
Fix
γ , solve for w1, · · · , wK
2.
Fix
w1, · · · , wK ,
minimize error w.r.t.
We an have a dierent
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
2
γ
γk for eah enter µk
17/20
Outline
•
RBF and nearest neighbors
•
RBF and neural networks
•
RBF and kernel methods
•
RBF and regularization
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
18/20
RBF versus its SVM kernel
Hi
SVM kernel implements:
sign
X
αn>0
2
αnyn exp −γ kx − xnk + b
SVM
RBF
Straight RBF implements:
sign
K
X
wk exp −γ kx − µk k
k=1
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
2
!
+b
Hi
19/20
RBF and regularization
RBF an be derived based purely on regularization:
N
X
n=1
h(xn) − yn
2
+λ
∞
X
k=0
ak
Z
∞
−∞
k
dh
dxk
2
dx
smoothest interpolation
AM
L
Creator: Yaser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Leture 16
20/20







![[Jean-Pierre Hansen, I.R. McDonald] Theory of Simple Liquids](http://s1.studylib.ru/store/data/006244007_1-e3cdabba82e7d567cc7967ad36f752fa-300x300.png)